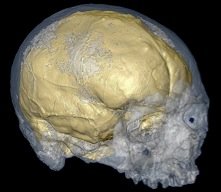
Finger points to new human
Thu, Mar 25 2010 08:07 | Palaeoanthropology | Permalink

A team of archaeologists have found the bone of a little finger while digging at Denisova Cave in the Altai Mountain, located in southern Siberia. The size of the bone suggests that it came from a child between five and seven years of age. It is difficult to distinguish between different species of humans based solely on the morphology of a single finger bone. However, the tentative dates put the age of the bone at between 30,000 and 50,000 years ago; a window of time when both Neandertals and modern humans coexisted in Eurasia.
In order to determine which species the little finger came from, Johannes Krause of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany sequenced the complete mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) from the finger bone and compared its DNA with that of modern humans and Neandertals. What they found surprised everyone involved in the project. The mtDNA of Denisova did not match that of modern humans or Neandertals. In fact it last shared a common ancestor with us and Neandertals in Africa around a million years ago.
We know of three major hominin migrations out of Africa. The first occurred with Homo erectus around 1.9 million years ago, followed by the ancestors of Neandertals sometime between 500,000 and 300,000 years ago, and finally modern humans around 50,000 years ago. This makes the Denisova specimen too late to be part of the Homo erectus exodus and too early to part of the other two.
However, it may be a little premature to declare this a new species of human. Svante Pääbo's team is already busy sequencing the nuclear DNA of the Denisova specimen. One, albeit unlikely, possibility is that this will turn out to be a representative of an outlier Neandertal population. Previous studies have found a wide diversity in both the morphology and mitochondria of geographically separated Neandertal populations. Until the nuclear DNA has been mapped it is not possible to definitively say if we are really dealing with a new species of human. However, if this does turn out to be the case, it would mean that we shared the globe with at least three other species of humans as late as 40,000 years ago.
View Comments
RSS woes
Due to some internal changes to my blog the RSS feed may have stop working for some subscribers. If your RSS feed for Ad Hominin is not updating correctly, please resubscribe using this link or by clicking on the "Subscribe to Ad Hominin" widget in the sidebar. Sorry for any inconvenience caused.
If you have not already subscribed to Ad Hominin now would be a good time to do so. It is a great way to keep up to date with any new posts.
If you have not already subscribed to Ad Hominin now would be a good time to do so. It is a great way to keep up to date with any new posts.
Why people believe in homeopathy
Mon, Mar 22 2010 04:16 | Scepticism | Permalink

How long will it take mankind to learn that while they listen to "the speaking hundreds and units, who make the world ring" with the pretended triumphs they have witnessed, the "dumb millions" of deluded and injured victims are paying the daily forfeit of their misplaced confidence!
Almost 170 years after Oliver Wendell Holmes read these words to the Boston Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge the pseudoscience of homeopathy continues to thrive. An EU commission statement estimates that some 30 million people in the EU use homeopathy, while the WHO estimates that around 500 million in the world use it.
Since Wendell Holmes' time a colossal body of evidence has been amounted showing that homeopathy has no medicinal effect beyond the placebo effect. The core concepts of homeopathy fly in the face of science and logic. homeopathy uses highly dilute solutions of a substance to treat disease. Most homeopathic solutions are so dilute that there is almost no chance that they will contain even a single molecule of the original active agent. Counterintuitively, homeopathic practitioners claim that the more dilute the solution, the stronger the homeopathic remedy. This contradicts the well-known phenomenon of dose response, which says that the more of a chemical an organism is exposed to, the greater the effect. Take one sleeping pill and it will help you sleep; take two and the effect is even more powerful; take 100 sleeping pills and you are not likely to wake up … ever! On the other hand, homeopaths would suggest that the more dilute the solution, the more "powerful" the effect. But how could a solution of something that doesn't contain even a single molecule of active ingredient have any effect? Here, things get even more bizarre. They suggest that water has memory. Seemingly, water has the ability to remember contact with certain substances, while at the same time being able to forget all the raw sewage and fecal matter that it has been in contact with. If homeopathy is nothing but water, why do so many people continue to believe it works?
Scientists and sceptics who engage with advocates of homeopathy usually end up throwing their hands up in the air in frustration. The reason is that most people who have come to believe in homeopathy do not do so based on scientific data or for particularly rational reasons. As such, it is unlikely that anyone who did not come to a particular position based on logic or reason will be argued out of that position using logic and reason. Indeed, no amount of rational argument will convince proponents of this modality that they are misguided. Holmes was well aware of the ineffectiveness such an exercise, stating that "… it is impossible not to realize the entire futility of attempting to silence this asserted science by the flattest and most peremptory results of experiment."
It is tempting to criticise such beliefs on the grounds that the people who hold them are somehow lacking basic cognitive skills. In fact, people who believe in all kinds of strange things are often very rational in other aspects of their life. I would instead argue that the faulty thinking that many engage in is a byproduct of our mind works. The human brain evolved not only to explain the world around us; it evolved to deal with an innumerable amount of tasks. Cultural transmission does not occur by downloading information, as was once believed, but rather is based on an inferential system. We classify things in our environment into ontological categories. Most things we encounter in our environment fall into one of the following groups: person, animal, natural object, tool and plant. Each ontological category has a set of characteristics that define it and set it apart from other categories. We make certain inferences about objects based on which ontological category it belongs to. For instance, we are not surprised when a dog walks down the street but would find it strange if we saw an oak tree doing so. Locomotion is part of our mental template for people and animals but not plants. We find certain counter-intuitive notions more memorable than blander ones, a prerequisite for a successful meme. Superstitious beliefs often combine ontological beliefs with a category violation. For instance, disembodied souls and inanimate statues that can cry, hear or bleed represent category violations for a person and a natural object respectively. However, not all superstitious beliefs are equally believable. While the belief in ghosts is widespread, the belief that ghosts cannot think and have desires is virtually non-existent. Violations must allow for further inferences, otherwise they result in cognitive dead ends. Although few of my readers literally believe in superheroes and zombies, that does not stop us from making inferences about what their needs, wants and limits would be if they did exist.
The idea that water has memory is a categorical violation. Memories are characteristic of a person or animal but not a natural object. Crucially, the belief that water has memory does not block further cognitive inferences. Conversely, we would find it much more difficult to believe that water remembers the substances that other water had been in contact with. This type of belief is rare since it prevents us from making further inferences. We have experience with the concept of remembering things that we have been in contact with but don't have experience of what it is like to remember things other people have been in contact with. People I met when I was younger — people who I have not seen for many years – still have an influence on me now. Likewise, it is not such a large cognitive leap to believe that substances that came into contact with water still have an influence over it.
Another important component of homeopathy is vitalism. The idea that we are more than just the aggregate of chemical and mechanical processes is an appealing one. Vitalism appeals to our core intuitions. Vitalists believe that the laws of science are inadequate to explain life processes. There must be something more to it – a soul or some elan vital. All of us operationally view ourselves as both body and mind, even those of us who outright reject the idea of a disembodied self or soul. The self is not something that governs the brain, rather the self is the outcomes of brain processes. However, our brain does a wonderful job of convincing us otherwise. The father of homeopathy, Samuel Hahnemann, saw the vital force as a "spirit like" force that maintained life. He believed that the inner vital force maintained the body's internal balance. When the body became ill it would push the illness outwardly, causing the symptoms of the disease or illness to manifest. Many homeopaths believe that all disease come down to one thing — the disturbance of the vital force. They believe that only homeopathic remedies stimulate the vital force into action.
Sympathetic or imitative magic is found in cultures the world over. Sympathetic magic is based on two related concepts: the law of similarity and the law of contagion. The former states that like things produce like effects, while the latter is the idea that items that have been in contact continue to affect each other. Perhaps the best known example of sympathetic magic is the use of voodoo dolls to place a curse on a specific person. Cargo cults would also engage in sympathetic magic by building landing strips and radio towers to encourage the airplanes that delivered them precious cargo during World War II to come back again. In the past, whooping cough and a sore throat were often treated by tying knots in a piece of string and hanging it around the ill person's neck. The knots were supposed to symbolise the tightness in the person's throat. Liverworts have been used for hundreds of years as a cure ailments of the liver, probably because of the plant's resemblance to the liver. A cure for pneumonia was to tie the lungs of a sheep to the soles of the feet of a patient. Golden objects and butter were commonly used as cures for jaundice. It was believed that warts could be cured by rubbing them on a frog, most likely because of the frog's warty appearance. The use of oysters, rhinoceros horns and tiger penises as aphrodisiacs are all examples of sympathetic thinking. The list goes on and on.
In a similar vein, homeopathy uses the concept of "like cures like." It is based on the idea that substances which produce symptoms similar to those of a particular illness can treat that illness. For instance, homeopaths may treat a person suffering from hay fever with an onion extract, since both produce watery eyes and a runny nose. The idea that water can still remember things it was previously in contact with, is an example of the "law of contagion." In this regard, homeopathy is similar to the concept of holy water that is common to many religions.
The brain processes that lead someone to believe in homeopathy exist in all of us. Our mental capacities evolved to aid in our survival, with erroneous beliefs an emergent property of our intuitive psychology. We are all prone to cognitive dissonance aversion, memory illusion, and confirmation bias. Such cognitive traps are probably adaptive and essential to mental well-being. The biologist Lewis Wolpert suggests that scientific thinking is in fact aberrant. Science is a conscious departure from intuition and common sense. Homeopathy is parasitic upon brain processes that originally evolved for other activities. If we want to understand why people believe in homeopathy, we must first understand how such beliefs enlist our evolved mental capacities.
References and further reading
Boyer, P (2001): Religion Explained. Evolutionary Origins of Religious Thought. New York: Basic Books.
Holmes OW (1842). Homœopathy, and its kindred delusions; two lectures delivered before the Boston society for the diffusion of useful knowledge, Boston: William D. Ticknor.
Wolpert, L (1993). The unnatural nature of science. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Above photo "Hot Raw Sewage" by Stuck in Customs is used under creative commons license.
Changes to commenting service
I have received notification that my comment service Haloscan will be closing. Unfortunately, there is no way to export older comments. Since my blog is relatively new and only gets a few comments, I think the move to a new comments system should be a minor inconvenience. With that said it hasn't been an easy decision. I will be migrating the comments to the Disqus service. Thanks to everybody who has commented on my past posts. Your feedback and comments are very important to me.
The upside of these changes means that I can use a plugin called RapidBlog that allows me to use the Google Blogger service to write and publish blog posts. Migrating to Blogger means that I'm no longer tied to my machine and can post while on the road. The main reason I didn't use this earlier was that it meant losing comments, which is now inevitable. Hopefully the move to Google Blogger will be invisible for you the reader. Thank you for your understanding and continued support.
The upside of these changes means that I can use a plugin called RapidBlog that allows me to use the Google Blogger service to write and publish blog posts. Migrating to Blogger means that I'm no longer tied to my machine and can post while on the road. The main reason I didn't use this earlier was that it meant losing comments, which is now inevitable. Hopefully the move to Google Blogger will be invisible for you the reader. Thank you for your understanding and continued support.
Four Stone Hearth 88
Wed, Mar 17 2010 05:21 | Anthropology | Permalink

Welcome to the St. Patrick’s Day special edition of Four Stone Hearth 88. Four Stone Hearth is a fortnightly anthropology blog carnival. Topics covered span the four major fields of anthropology: archaeology, socio-cultural anthropology, bio-physical anthropology and linguistic anthropology. If you would like to host the carnival, please write to . The next issue will be hosted at the Greg Laden’s blog on 31 March.
Online Degrees.net has posted their 100 best blogs for anthropology students. It is a wonderful resource that I recommend checking out. Now on with this round of carnival posts.
Archaeology
Luis over at the blog Leherensuge reports on the alleged archaeological forgery at Glozel. The controversy revolves around a hoard of objects that appear to date from different time periods. The death of the principle protagonist, Emile Fradin, has renewed interest in these alleged artefacts. Are these the genuine article or just another Piltdown. Decide for yourself.
Over at Testimony of the spade, Magnus Reuterdahl reflects on how extant abbeys can give us a greater appreciation for those which over time have falling into ruin.
Martin Rundkvist over at Aardvarchaeology, has mixed feelings about his Magnum opus entitled "Domed oblong brooches of Vendel Period Scandinavia.” Martin relays how sticking to your “scholarly ideals” is not always the easiest road to career advancement.
Biological anthropology
In a recent post, I discuss the trend towards decreased head size starting around 30,000 years ago, which continues today.
Carl Feagans at ahotcupofjoe looks at the dispersal of early Homo out of Africa.
Last year, amidst much media fanfare everybody came to know about our 47 million year old purported ancestor “Ida”. This was indeed a spectacularly preserved fossil specimen, which preserved the outline of the body as well as the stomach contents. However, the scientific community at the time aired scepticism about the claim that it was on the evolutionary line that led to us. Many palaeontologists and primatologists were quick to point out that this primate looked more lemur-like. Well, it turns out that they were right. In a paper published in the Journal of Human Evolution shows that this species, Darwinius masillae, belonged to an extinct branch of primates, most closely related to lemurs and lorises. Brian Switek of the Laelaps gives a synopsis of the paper, while Eric Michael Johnson at Primate Diaries gives a very accessible account of the whole affair.
John Hawks is a fly on the wall at a symposium on genetics and genealogy of the African Diaspora. He reports on Fatimah Jackson’s genetic work in Africa and African-Americans, in particular the idea of "ethnogenetic layering”.
Raymond Ho at the Prancing Papio blog has a review of a paper on the changing mating systems in Sichuan snub-nosed monkeys. The pieces offers some plausible evolutionary reasons for the shift from polygynous to polygamous mating systems.
Linguistic anthropology
Valerie Williamson writes about Siberian languages, which are on the verge of extinction. The race is on for linguists to document these languages before they disappear completely.
Socio-cultural anthropology
In the spirit of the occasion, anthropologyworks has compiled a bibliography of social anthropology articles on Ireland and the Irish.
Krystal, over at Anthropology in Practice, talks about a street vendor in her city that has started to take coffee orders via text message. Is this merely a fad or society simply adapting to our greater reliance on digital media?
Ronald Kephart a.k.a. the Cranky Linguist reports on the educational malpractice of teaching religion as science at Liberty University.
Also check out Eric’s article on Coca Cola’s over-exploitation of water resources in India. It seems that the slogan “Good Till the Last Drop" has a more pernicious meaning.
A Very Remote Period Indeed has a wonderfully titled piece “Mad Neanderthals, peer review and scholarly publication”. Controversy has surrounded the journal Medical Hypotheses since its very conception. This journal is unique in that it doesn’t have a peer review system, while promoting controversial and thought-provoking ideas. However, Julien Riel-Salvatore tells of the comment he published in this journal in response to an article that proposed that Spongiform Encephalopathies may have led to the demise of the Neanderthals. Julien does not think the biggest problem is with the journal’s incredibly low standards but rather with the academic publishing house Elsevier, who by purchasing Medical Hypotheses has given it an air of legitimacy.
That’s it for another edition of Four Stone Hearth. Happy St. Patrick’s Day to one and all!
Image Credits
Golden snub nosed monkey from artsonearth,
CocaColaIndia by Carlos Latuff under the Wikimedia Commons licence.
Marilyn Monroe reading James Joyce. Flickr creative commons licensed content by user I, Puzzled.
The incredible shrinking human brain
Sun, Mar 14 2010 05:12 | Palaeoanthropology | Permalink
The Times Online recently ran a story about a French team that have made an endocast by digitally scanning inside the skull of Cro-Magnon 1, perhaps the most famous of all Upper Palaeolithic skulls. The mould of Cro-Magnon highlights what has been long known about these European early modern humans since their first discovery in 1868 - they had bigger brains than us. In fact, average human brain size has been decreasing during the last 30,000 or so years. This revelation was rather troubling for nineteenth-century anthropologists who sought to link brain size with intelligence. Not only did these early modern humans have a larger brain volume than us, but so too did the Neanderthals, who were regarded by many at the time as “a barbarous and savage race” (Schaaffhausen 1858). To add injury to insult, the decrease in head size coincides with some of the greatest cultural innovations in human history.
The Times article forwards a number of the various hypotheses about why brain size has decreased. Antoine Balzeau reasons that “the cerebellum — a brain structure linked to language and concentration — appears to take up a larger proportion of the head now than in the time of Cro Magnon 1.” While it is true that the cerebellum is proportionally larger in modern humans, it is proportionally smaller than in apes, by around 20%. We still don’t know enough about brain function to be able to say what advantage, if any, a larger cerebellum would give us.
Second up, is the suggestion that big heads are somehow an adaptation to cold climate. There are a number of problems with this idea. If having a large skull is an adaptation to cold environments we would expect to see such traits peaking in the aftermath of the Last Glacial Maximum around 20,000 years ago, many millennia after Cro-Magnon walked the earth. As a general rule people living in Arctic regions tend to have more rounded heads, unlike the long headed Cro-Magnon. What’s more, the limbs of Cro-Magnon and their kin are quite long, contradicting Allen’s Rule which predicts that species will evolve smaller appendages as an adaptation to colder climes. Their body type also differs markedly from that of Neandertals, for whom there is a better case to made of being cold-adapted.
The article goes on to suggest diet as a driving force behind the decrease in head size. Cranial robusticity has indeed been shown to correlate with diet. It is important, however, to make the distinction between cranial size and robusticity. While the two are related they do not necessarily go hand in hand. While the Gravettian populations were undoubtedly more robust than most modern-day populations, they are not especially robust when compared to the Mesolithic populations of Téviec and Hoëdic or modern Aboriginal Australian or Fuegian populations. It is also unclear what dietary innovation could account for the decrease in head size. We have unambiguous evidence for the control of fire at around 250,000 years ago, while agriculture did not appear until around 10,000 years ago. The dates just don’t add up.
The article suggest one more hypothesis for the downsizing of the brain: “… with high infant mortality, only the toughest survived — and the toughest tended to have big heads.” Infant mortality is an ever-present problem for humans because bipedalism has constrained the size of the birth canal. If anything, giving birth to a larger headed children is going to lead to increased mortality for both the mother and child. Indeed, natural selection has restricted in utero brain growth in humans, with a large proportion of brain development occurring outside of the womb. In most non-human primates, the brain is close to adult size by the first year of life. In humans, on the other hand, near-adult brain size is not reached until about ten years of age.
Perhaps, the best explanation for the larger head size of our ancestors is one that the authors failed to mention – allometry. Bigger animals have bigger brains. While the cranial capacity for modern humans is large for a primate of our size, it is still only about a quarter of the size of that of an elephant. The decrease in brain size during the late Pleistocene was also accompanied by a decrease in body size. In other primates that show a decrease in brain size, there is an accompanying decrease in body size. Having a larger brain comes at a cost. The brain is a greedy glucose-guzzling tissue. The is possible that our smaller brain has allowed us to reallocate energy for other bodily functions.
References and further reading
Henneberg M. Evolution of the human brain: is bigger better?. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 1998, 25:745-749.
Schaaffhausen H. On the crania of the most Ancient Races of Man. Müllers Archiv 1858:453.
Ruff C, Trinkaus E, Holliday T. Body mass and encephalisation in Pleistocene Homo. Nature 1997: 387: 173–6.

The Times article forwards a number of the various hypotheses about why brain size has decreased. Antoine Balzeau reasons that “the cerebellum — a brain structure linked to language and concentration — appears to take up a larger proportion of the head now than in the time of Cro Magnon 1.” While it is true that the cerebellum is proportionally larger in modern humans, it is proportionally smaller than in apes, by around 20%. We still don’t know enough about brain function to be able to say what advantage, if any, a larger cerebellum would give us.
Second up, is the suggestion that big heads are somehow an adaptation to cold climate. There are a number of problems with this idea. If having a large skull is an adaptation to cold environments we would expect to see such traits peaking in the aftermath of the Last Glacial Maximum around 20,000 years ago, many millennia after Cro-Magnon walked the earth. As a general rule people living in Arctic regions tend to have more rounded heads, unlike the long headed Cro-Magnon. What’s more, the limbs of Cro-Magnon and their kin are quite long, contradicting Allen’s Rule which predicts that species will evolve smaller appendages as an adaptation to colder climes. Their body type also differs markedly from that of Neandertals, for whom there is a better case to made of being cold-adapted.
The article goes on to suggest diet as a driving force behind the decrease in head size. Cranial robusticity has indeed been shown to correlate with diet. It is important, however, to make the distinction between cranial size and robusticity. While the two are related they do not necessarily go hand in hand. While the Gravettian populations were undoubtedly more robust than most modern-day populations, they are not especially robust when compared to the Mesolithic populations of Téviec and Hoëdic or modern Aboriginal Australian or Fuegian populations. It is also unclear what dietary innovation could account for the decrease in head size. We have unambiguous evidence for the control of fire at around 250,000 years ago, while agriculture did not appear until around 10,000 years ago. The dates just don’t add up.
The article suggest one more hypothesis for the downsizing of the brain: “… with high infant mortality, only the toughest survived — and the toughest tended to have big heads.” Infant mortality is an ever-present problem for humans because bipedalism has constrained the size of the birth canal. If anything, giving birth to a larger headed children is going to lead to increased mortality for both the mother and child. Indeed, natural selection has restricted in utero brain growth in humans, with a large proportion of brain development occurring outside of the womb. In most non-human primates, the brain is close to adult size by the first year of life. In humans, on the other hand, near-adult brain size is not reached until about ten years of age.
Perhaps, the best explanation for the larger head size of our ancestors is one that the authors failed to mention – allometry. Bigger animals have bigger brains. While the cranial capacity for modern humans is large for a primate of our size, it is still only about a quarter of the size of that of an elephant. The decrease in brain size during the late Pleistocene was also accompanied by a decrease in body size. In other primates that show a decrease in brain size, there is an accompanying decrease in body size. Having a larger brain comes at a cost. The brain is a greedy glucose-guzzling tissue. The is possible that our smaller brain has allowed us to reallocate energy for other bodily functions.
References and further reading
Henneberg M. Evolution of the human brain: is bigger better?. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 1998, 25:745-749.
Schaaffhausen H. On the crania of the most Ancient Races of Man. Müllers Archiv 1858:453.
Ruff C, Trinkaus E, Holliday T. Body mass and encephalisation in Pleistocene Homo. Nature 1997: 387: 173–6.
Four Stone Hearth submissions
Sat, Mar 13 2010 02:48 | Anthropology | Permalink
I will be hosting a St. Patrick’s Day special edition of Four Stone Hearth on Wednesday, March 17th. Four Stone Hearth is a fortnightly anthropology blog carnival. If you have read or written any interesting blog posts on archaeology, socio-cultural anthropology, bio-physical anthropology or linguistic anthropology in the last few weeks, please a link and I’ll be sure to include them.
100 best anthropology blogs
Tue, Mar 9 2010 12:47 | Anthropology | Permalink
The Online Degrees.net blog has compiled a comprehensive list of the 100 Best Blogs for Anthropology Students. This is a fantastic resource for anybody interested in anthropology.
Paleo diet
Sun, Jan 24 2010 06:00 | Scepticism | Permalink
For many people the new year represents an occasion to set the clock back to zero and make a fresh start. We invariably eat too much during the festive season, only later to feel remorse for our gluttonous ways. With the new year comes the renewed goal of losing some of the extra padding. There are no end of miraculous sounding diets which promise to convert fat to flat. Among the various in vogue diets is the so-called Paleo diet (short for Paleolithic diet), also known as the caveman diet. The central premise behind the Paleo diet is that many human adaptations evolved during the Palaeolithic, and as such, we are maladapted to the modern world in which we find ourselves.
The premises of the Paleo diet raise some interesting questions that are well worth exploring. For instance, are we really better adapted to the Palaeolithic than the modern era and which aspects of the Palaeolithic does the Paleo diet reference? Many proponents ask the question “who ever heard of a fat caveman?”, as if the answer is somehow inferred. While it is seems be the case that the average Palaeolithic human had a brawnier body than the average modern human, we should not confuse correlation with causation. A better question to ask is whether the “caveman” physique is due solely to diet or are there other factors at play?
While certain human adaptations undoubtedly arose during the Palaeolithic, these are likely to be no more or less important than the adaptations of preceding and subsequent periods in our evolutionary history. Most of our genes evolved a long time before our ancestors were recognisable as primates, never mind humans. Moreover, humans continue to adapt to their diet today. Lactose tolerance is a good example of a trait that arose in many populations of humans after the Palaeolithic. Evolution exists on a continuum; it didn’t start and end sometime during the Palaeolithic.
The Palaeolithic covers a period of around 2.5 million years, as well as an immense geographic range. Moreover, many species of humans lived in very diverse environments during this time. Proponents of the Paleo diet rarely specify what period and indeed which populations or species they use as their model. Food procurement methods changed dramatically over this time period. Over the course of the Palaeolithic, humans shifted from mostly scavenging their meat to systematic hunting. Even among modern hunter-gatherers there is great dietary variation. For instance, the diets of Inuits and Aboriginal Australians couldn’t be more different. Another consideration is that humans have been selectively breeding plants and animals over many millennia. Many of the domesticated varieties we see today are unrecognisable from their wild ancestors. As such, while the Paleo diet recommends greater reliance on meats and non-cultivated plants, it should be kept in mind that these probably bear little resemblance to the wild species our ancestors ate.
The limb bones of the early Upper Palaeolithic Gravettian people are not only large but also have massive muscle attachments. Early humans were physically fit not only because of their diet but in large part due to their high mobility. Hunting and foraging expeditions would have required these groups to cover large distances. Demographic pressures impinging on these small bands of humans would also have further encouraged greater mobility.
It is not disputed that the diet of early hunter-gatherers was much more varied than that of their agricultural counterparts. Early agriculturalists often had an over reliance on few food types, leading to various nutritional deficiencies and generally poorer health. However, there is little reason why this should be the case today. Our shops and markets are packed with varieties of food that our ancestors would be only able to dream off.
Many of the recommendations of the Paleo diet are sensible, such as eating less processed foods, decreasing our sugar intake and increasing our dietary fibre. In this regard, the Paleo diet is on par with most governmental dietary recommendations. Why the need to dress it up in some romanticised account of how our ancestors ate? I will concede that versions of the Paleo diet are probably healthier than the diets most of us adhere to. However, the reasoning behind it is based on an immutable view of human prehistory, coupled with some poor evolutionary thinking.

Above photo modified from original by Lord Jim under creative commons license.
The premises of the Paleo diet raise some interesting questions that are well worth exploring. For instance, are we really better adapted to the Palaeolithic than the modern era and which aspects of the Palaeolithic does the Paleo diet reference? Many proponents ask the question “who ever heard of a fat caveman?”, as if the answer is somehow inferred. While it is seems be the case that the average Palaeolithic human had a brawnier body than the average modern human, we should not confuse correlation with causation. A better question to ask is whether the “caveman” physique is due solely to diet or are there other factors at play?
While certain human adaptations undoubtedly arose during the Palaeolithic, these are likely to be no more or less important than the adaptations of preceding and subsequent periods in our evolutionary history. Most of our genes evolved a long time before our ancestors were recognisable as primates, never mind humans. Moreover, humans continue to adapt to their diet today. Lactose tolerance is a good example of a trait that arose in many populations of humans after the Palaeolithic. Evolution exists on a continuum; it didn’t start and end sometime during the Palaeolithic.
The Palaeolithic covers a period of around 2.5 million years, as well as an immense geographic range. Moreover, many species of humans lived in very diverse environments during this time. Proponents of the Paleo diet rarely specify what period and indeed which populations or species they use as their model. Food procurement methods changed dramatically over this time period. Over the course of the Palaeolithic, humans shifted from mostly scavenging their meat to systematic hunting. Even among modern hunter-gatherers there is great dietary variation. For instance, the diets of Inuits and Aboriginal Australians couldn’t be more different. Another consideration is that humans have been selectively breeding plants and animals over many millennia. Many of the domesticated varieties we see today are unrecognisable from their wild ancestors. As such, while the Paleo diet recommends greater reliance on meats and non-cultivated plants, it should be kept in mind that these probably bear little resemblance to the wild species our ancestors ate.
The limb bones of the early Upper Palaeolithic Gravettian people are not only large but also have massive muscle attachments. Early humans were physically fit not only because of their diet but in large part due to their high mobility. Hunting and foraging expeditions would have required these groups to cover large distances. Demographic pressures impinging on these small bands of humans would also have further encouraged greater mobility.
It is not disputed that the diet of early hunter-gatherers was much more varied than that of their agricultural counterparts. Early agriculturalists often had an over reliance on few food types, leading to various nutritional deficiencies and generally poorer health. However, there is little reason why this should be the case today. Our shops and markets are packed with varieties of food that our ancestors would be only able to dream off.
Many of the recommendations of the Paleo diet are sensible, such as eating less processed foods, decreasing our sugar intake and increasing our dietary fibre. In this regard, the Paleo diet is on par with most governmental dietary recommendations. Why the need to dress it up in some romanticised account of how our ancestors ate? I will concede that versions of the Paleo diet are probably healthier than the diets most of us adhere to. However, the reasoning behind it is based on an immutable view of human prehistory, coupled with some poor evolutionary thinking.
Above photo modified from original by Lord Jim under creative commons license.
Dangerous quote mines: a cautionary tale

However, what happened Matt is much more disturbing. It has been long known that sauropods have a swelling in the sacral region, leading some people to suggest that it may have functioned as a second brain. This idea has been thoroughly debunked. When Matt was asked to comment on this here is how the original unedited conversation went down:
”Ok one of the curious things about sauropods is that they did have a swelling in the spinal cord in the neighbourhood of their pelvis. And for a while it was thought that may be this was sort of like a second brain to help control the back half of the body. Erm there are a couple of misconceptions there. One is that most animals control large part of their body with their spinal cord. If you’re going through day to day operations like just walking down the street and your minds on something else your brain isn’t even involved in very much controlling your body. A lot of that is a reflex arc that’s controlled by your spinal cord. So it’s not just dinosaurs that are controlling their body with their spinal cord, it’s all animals. Now the other thing about this swelling at the base of the tail is we find the same thing in birds and its called the glycogen body. It’s a big swelling in the spinal cord that has glycogen which is this very energy rich compound that animals use to store energy. Problem is we don’t even know what birds are doing with their glycogen bodies. Er the function is mysterious – we don’t know if the glycogen is supporting their nervous system – if its there to be mobilised, help drive their hind limbs or the back half of their body and until we find out what birds are doing with theirs we have very little hope of knowing what dinosaurs were doing with their glycogen bodies.”
I can only imagine the shock Matt experienced when this got edited down to:
“This was sort of like a second brain to help control the back half of the body.”
This is not what he said at all. In fact, he said the exact opposite, even going so far as to give the reasons why this is a discredited theory. Not only is this downright dishonest on the part of the producers, it also calls into question the credibility of this professional scientist. More generally, it gives legitimacy to the ‘second brain’ hypothesis in the eyes of the public. Understandably, enraged by what he saw, Matt sent an email form Dangerous Ltd, the production company who were responsible for filming the documentary. He received a reply that amounted to a nopology, even having the audacity to say: “we were simply working on the show ever aware of the demands of our audience.” And what about presenting the facts or fairly representing the views of the scientists?
Thankfully, this story has a happy ending. Matt talked to a person high up at the Discovery Channel, who promised that the egregious portion would be promptly removed. Unfortunately, this misrepresentation of a scientist is not an isolated case and we would do well to understand why this happens and what can be done to prevent it. The first thing we should remember is that documentaries are, first and foremost, made for entertainment. As a result, most are written by screenwriters and have a predetermined script. One would think that the scientific facts write themselves but this is sadly not the case. It is the job of the film crew to interview specialists, all the time being conscious of the preplanned plot. Scientists should not be afraid to ask to see an outline of the plot. That way they have an idea of what pieces of information the production team are after. When documentary makers interview scientists they are generally looking for snippets that will propel the storyline. This is the reason why hours of footage eventually get edited down to mere seconds. Naturally, the more time you spend talking the greater the chances of something making it into the finally cut. However, this also means that there is more material that can be taken out of context. It is in the interviewee’s best interest to keep the conversation from wandering off course. This can be achieved by negotiating an hourly fee with the production company prior to any interview. Scientists shouldn’t be shy about demanding money for their time. Film crews will often have a budget for this but are normally not very forthcoming in divulging this information. As long as the film crew are cognisant of their budget, they are more likely to cut to the chase earlier on, rather than fishing around for juicy quotes.
While it is tempting for experts to point out the flaws in refuted hypotheses, they are perhaps better off biting their tongues. This way, their words cannot be contorted to suggest that they are in fact a proponent of a viewpoint they firmly disagree with. However, if you are cornered into giving an opinion on a contrary idea it is perhaps best to let your body do the talking. If you can visibly demonstrate your disdain for a particular idea through your facial expressions, it makes it much harder for the editors to later manipulate your words in such a way that they contradict your body language. This requires scientists to really show and perhaps exaggerate their emotions, but heck, if one truly loves their profession that shouldn’t be too difficult to accomplish.
It is important that scientists speak out against any media distortions of science. It is likely that Dangerous Ltd. felt some heat from the negative reaction of bloggers and commentators, subsequent to Matt’s initial blog post. If we don’t take a stand, we are simply emboldening sloppy science communication. We should email, phone, or write to these companies and let them know that we are not happy with how science is being misrepresented. As a last resort one may consider taking legal action. While scientists give up many of their privileges once they sign a release form, slander is still slander, and as such is subject to legal action.
Good science doesn’t need to be dressed up or distorted, most especially when we are talking about dinosaurs. While some may cringe at the very thought, scientists more than ever before need to become media-saavy. The media is ultimately interested in a great story and will go to extreme lengths to get it. The case of Matt is not new and their will be many more cases like it to come. Only by being more aware of how the media operates can scientists be equipped to deal with such future misrepresentations.
Related reading
Lies, damned lies, and Clash of the Dinosaurs
Clash of the Dinosaurs: Dangerous Ltd document their own dishonest editing
Clash of the Dinosaurs: The Discovery Channel steps up
A scientist is QUOTE MINED on a Discovery dinosaur documentary